To help accelerate SD-WAN market growth and enable the creation of powerful, new hybrid networking solutions optimized for digital transformation, MEF published the industry’s first global standard defining an SD-WAN service and its service attributes—MEF 70. An update to that standard—MEF 70.1—includes new service attributes for underlay connectivity services, new measurable performance metrics that provide visibility into an application’s performance within the provider network and across multiple service providers, and the infrastructure to support application-based security.
We created the SD-WAN service standard within the context of our MEF 3.0 Global Services Framework. Combining standardized SD-WAN service with dynamic high-speed underlay connectivity services enables service providers to offer solutions with unprecedented user- and application-directed control over network resources and service capabilities.
SD-WAN is the way to interface policy with an intelligent software-defined network. Standardization makes it easier for integration to work across multiple types of underlying transport services. Ultimately, the combination of standardized and orchestrated overlay and underlay services provide a better customer experience, with improved service capabilities, and guaranteed resiliency.
See MEF’s Technical Standards & Educational Materials for SD-WAN
2024 State of the Industry Report: SASE
The risk of major cyberattacks has never been greater. Organizations are responding by making cybersecurity a top priority for digital technology investment. Find out how…
The diagram below illustrates all of the definitive components that together help define a standard MEF 3.0 SD-WAN service. One of the key elements is the SD-WAN Edge, which is a function existing at the subscriber site, e.g. an enterprise customer premises, that connects the SD-WAN user-to-network interface (UNI) to the underlay connectivity service (UCS) UNI. This function applies policies to the IP packets entering the SD-WAN service, determining how they are classified into application flows and forwarded across the underlay connectivity services according to the policy configuration.
Much like MEF’s service standards for underlay connectivity, an SD-WAN service consists of SD-WAN end points, specifically SD-WAN Virtual Connection End Points that together form the SD-WAN Virtual Connection. These end points represent the demarcation between the responsibility of the SD-WAN service provider and the subscriber. As an overlay service, SD-WAN involves multiple underlay connectivity services. In the sample below, there are two such services, which can leverage either MEF 3.0 underlay connectivity services, like Carrier Ethernet or other services, for example, an Internet broadband service. Furthermore, a unique element of SD-WAN services is the ability to forward traffic directly to the Internet from an SD-WAN UNI, which is termed Internet Breakout.
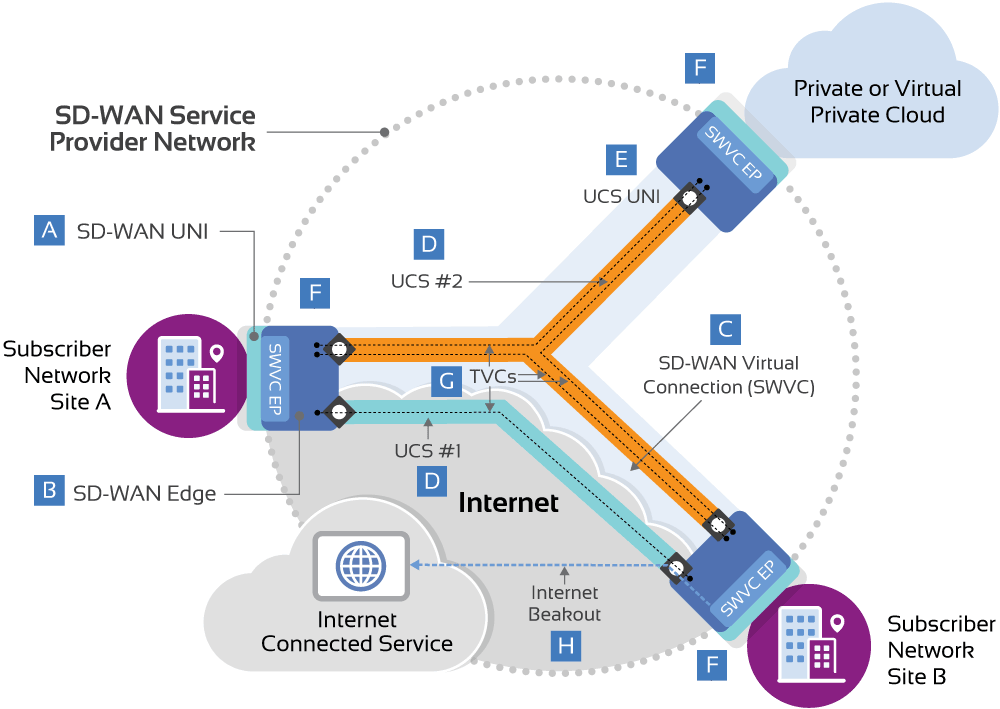
Demarcation between Service Provider and Subscriber responsibility.
Connects SD-WAN UNI to UCSs, maps packets to application flows, enforces policies, and selects TVC, over which to forward each flow.
Logical multipoint connection between the SD-WAN UNIs, which corresponds to the SD-WAN Service.
Any WAN service used by the SD-WAN, e.g., MEF Ethernet Services (MEF 6.2), MEF IP Services (MEF 61.1), MPLS VPNs and Internet Access, and MEF Optical Transport Services (MEF 63).
Any WAN service used by the SD-WAN, e.g., MEF Ethernet Services (MEF 6.2), MEF IP Services (MEF 61.1), MPLS VPNs and Internet Access, and MEF Optical Transport Services (MEF 63).
Demarcation between the service provider of the underlay connectivity service, and the subscriber responsibility.
Point-to-point paths across UCSs that compose an SD-WAN Service.
Logical point where application-flow policies are assigned and applied.
Logical point where application-flow policies are assigned and applied.
Logical point where application-flow policies are assigned and applied.
Application flows forwarded from an SD-WAN UNI directly to the Internet rather than delivered to another SD-WAN UNI.
ASD-WAN User-to-Network Interface (SD-WAN UNI)
Demarcation between Service Provider and Subscriber responsibility.
BSD-WAN Edge
Connects SD-WAN UNI to UCSs, maps packets to application flows, enforces policies, and selects TVC, over which to forward each flow.
CSD-WAN Virtual Connection (SWVC)
Logical multipoint connection between the SD-WAN UNIs, which corresponds to the SD-WAN Service.
DUnderlay Connectivity Service (UCS)
Any WAN service used by the SD-WAN, e.g., MEF Ethernet Services (MEF 6.2), MEF IP Services (MEF 61.1), MPLS VPNs and Internet Access, and MEF Optical Transport Services (MEF 63).
EUCS User-to-Network Interface (UCS UNI)
Demarcation between the service provider of the underlay connectivity service, and the subscriber responsibility.
FSD-WAN Virtual Connection End Point (SWVC EP)
Logical point where application-flow policies are assigned and applied.
GTunnel Virtual Connection (TVC)
Point-to-point paths across UCSs that compose an SD-WAN Service.
HInternet Breakout
Application flows forwarded from an SD-WAN UNI directly to the Internet rather than delivered to another SD-WAN UNI.
MEF 3.0 SD-WAN & SASE – Frequently Asked Questions — 2021 Dec
Product Portfolio: SASE, SD-WAN, Overlay Services
Tags: Certification
MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Services & SASE – Frequently Asked Questions
MEF 3.0 Workshop – Digital Services Expertise – New MEF SD-WAN Certified Professional (MEF-SDCP) — 2019 Nov
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN Certification, SD-WAN
Addressing the skills gap challenge is tantamount to successfully navigating the industry's digital transformation. MEF's SD-WAN Certified Professional designation validates the knowledge required to design, engineer, operate and solution MEF managed SD-WAN services.
MEF 3.0 Workshop – MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Certification — 2019 Nov
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN Certification, SD-WAN
MEF's SD-WAN Certification serves to accelerate market adoption of managed SD-WAN services by validating compliance with industry-designed and delivered standards for delivering managed SD-WAN as well as the underlying technology.
MEF 3.0 Workshop – MEF 3.0 SD WAN Services — 2019 Nov
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN
In July 2019, MEF published the industry’s first global standard defining an SD-WAN service and its service attributes to help accelerate SD-WAN market growth and facilitate creation of powerful new hybrid networking solutions that are optimized for digital transformation.
MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Services — 2019 Nov
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN
Tags: Also in Mandarin, Also in Spanish
This White Paper is intended for SD-WAN Service Providers and their enterprise customers who want to understand what a standardized, managed SD-WAN service is and the benefits it brings to the industry.
MEF 70.2 SD-WAN Service Attributes and Service Framework — 2023 Oct
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN
The SD-WAN Service Attributes and Service Framework Standard defines the externally visible behavior of a MEF SD-WAN Service.
MEF 131 Draft Release 1 MEF Secure SD-WAN Certification Test Requirements — 2022 May
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN Certification, SD-WAN
This document describes the MEF Secure SD-WAN certification test requirements to validate conformance with the Application Flow Security for SD-WAN Services (MEF 88) [3]. The Secure SD-WAN Certification Test Requirements standard is functional, and hence implementation-independent.
MEF 88 Application Security for SD-WAN Services — 2021 Nov
Product Portfolio: SASE, SSE, SSE Certification, SD-WAN
This Standard specifies the requirements needed to add Application Flow Security to SD-WAN Services.
MEF 70.1 SD-WAN Service Attributes and Service Framework — 2021 Nov
Amendments: MEF 70.2
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN Certification, SD-WAN
The SD-WAN Service Attributes and Service Framework Standard defines the externally visible behavior of SD-WAN Services. A Service deployment is based on an agreement between an SD-WAN Subscriber (the buyer) and an SD-WAN Service Provider (the seller) that includes agreement on the values of a set of SD-WAN Service Attributes defined in this document.
MEF 70 SD-WAN Service Attributes and Services — 2019 Jul
Product Portfolio: SD-WAN
The SD-WAN Service Attributes and Services Standard defines the externally-visible behavior of SD-WAN Services. The Service description is based on an agreement between an SD-WAN Subscriber (the buyer) and an SD-WAN Service Provider (the seller) that includes agreement on the values of a set of SD-WAN Service Attributes defined in this document.
I want to investigate further. See all SD-WAN resources:
Adopting MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Services standards empowers service providers to unlock new overlay digital services potential and best adapt to the application-centric needs of your enterprise customers. Enterprises can, in turn, quickly assess and verify the foundational components and service attributes of a certified SD-WAN service to fully address business requirements. In addition, a MEF-certified SD-WAN service is future-proofed to enable dynamic and automated capabilities supporting operational and control-related interactions related to the service.
As a MEF member, you have access to all the standards work, including incubation projects, pre-release standards, and working drafts. Engage with your industry peers and lend your voice to the SD-WAN standards development. Our current initiatives are available in the MEF 3.0 SD-WAN Service Hub on the MEF Members’ Wiki.
All employees of active MEF-member companies are authorized to access MEF Members’ Wiki. Don’t have a login? Register. Not a member? Join MEF. Not sure? Contact Us.
Go to the Member Wiki