Optical Transport Services revenue is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 8.5% through to 2023, with an estimated 4.9 billion USD market in 2023. High bandwidth, high performance point-to-point connectivity services are critical to meet the demands of large enterprises for applications such as Data Center Interconnect. MEF has addressed this need by being the only industry organization to define standardized Layer 1 connectivity services, a.k.a. Optical Transport Services. Coupled with MEF’s Lifecycle Service Orchestration (LSO) framework, service providers achieve faster time-to-revenue and lower operating costs while meeting the business needs of the enterprise.
See MEF’s Technical Standards & Educational Materials for Optical Transport
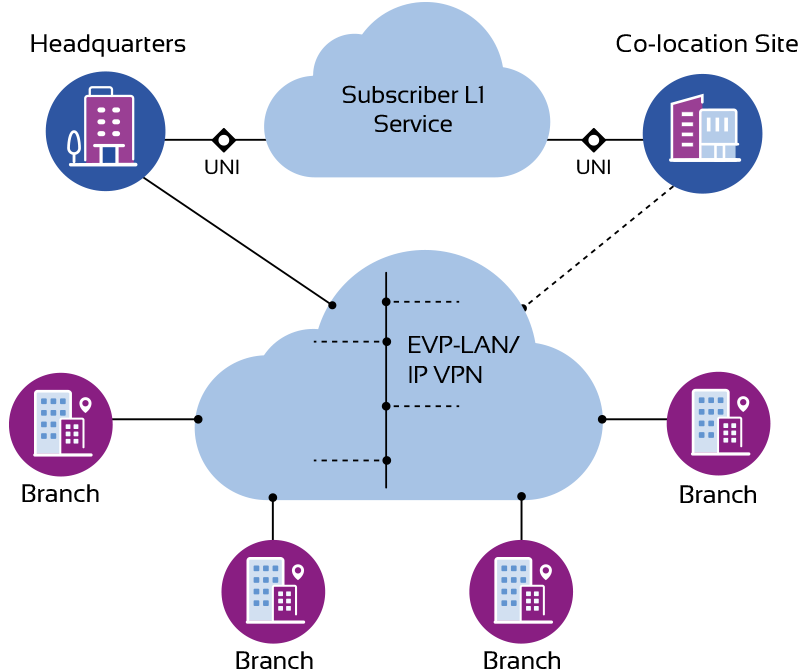
An enterprise, such as a financial service company, uses a multi-point network to connect multiple sites, such as between its branches and headquarters. To support business continuity, the company establishes back-up computing and storage at a co-location site, and leases a Subscriber L1 Service (the technical term for a MEF 3.0 Optical Transport service that’s connected to an end user of that service, such as an enterprise) to connect headquarters to the co-location site, enabling ultra-high-speed connectivity to maintain redundancy between HQ and the co-location facility.
This diagram exemplifies an end-to-end service supporting disaster recovery and high-availability with Optical Transport services, in addition to a Carrier Ethernet service for the branch locations. In MEF technical parlance, optical transport services are called Layer 1 (or L1) services and are either Subscriber services for direct end use, or Operator services that are used by another service provider.
Orchestrated MEF 3.0 Optical Transport Services — 2020 Mar
Product Portfolio: Optical Transport
MEF is the first industry body to publish standards for Optical Transport services and their orchestration.
MEF 3.0 Workshop – MEF 3.0 Optical Transport Services — 2019 Nov
Product Portfolio: Optical Transport
In 2018, MEF published its first Optical Transport services standard (MEF 63) for subscriber services that support Ethernet and Fibre Channel client protocols as well as SONET/SDH client protocols for legacy WAN services.
MEF 64 Operator Layer 1 Service Attributes and Services — 2020 Feb
Product Portfolio: Optical Transport
The Service Attributes of an Operator Layer 1 Service observable at a Layer 1 User Network Interface and a Layer 1 External Network Network Interface are defined.
MEF 63 Subscriber Layer 1 Service Attributes — 2018 Aug
Product Portfolio: Optical Transport
The attributes of a Subscriber Layer 1 Service observable at a Layer 1 User Network Interface (L1 UNI) and from a L1 UNI to a L1 UNI are defined. In addition, a framework for defining specific instances of a Subscriber Layer 1 Service is described.
I want to investigate further. See all Optical Transport resources:
From an enterprise perspective, having a standard service definition for optical transport, (a.k.a. wavelength service) enables effective comparison of offerings and their attributes from different service providers. It also provides the subscriber with a means to clearly communicate their service requirements.
As for the providers themselves, they can transform from ad-hoc interconnection agreements to simplified and faster end-to-end service delivery.
A broad range of MEF standards and educational materials in the area of Optical Transport Services covering modeling, subscriber services, and operator services are available here. In addition, many related initiatives are accessible on the MEF Members’ Wiki.
All employees of active MEF-member companies are authorized to access MEF Members’ Wiki. Don’t have a login? Register. Not a member? Join MEF. Not sure? Contact Us.
Go to the Member Wiki